Overview 1. The core switching unit adopts a solid-sealed pole design, miniaturized
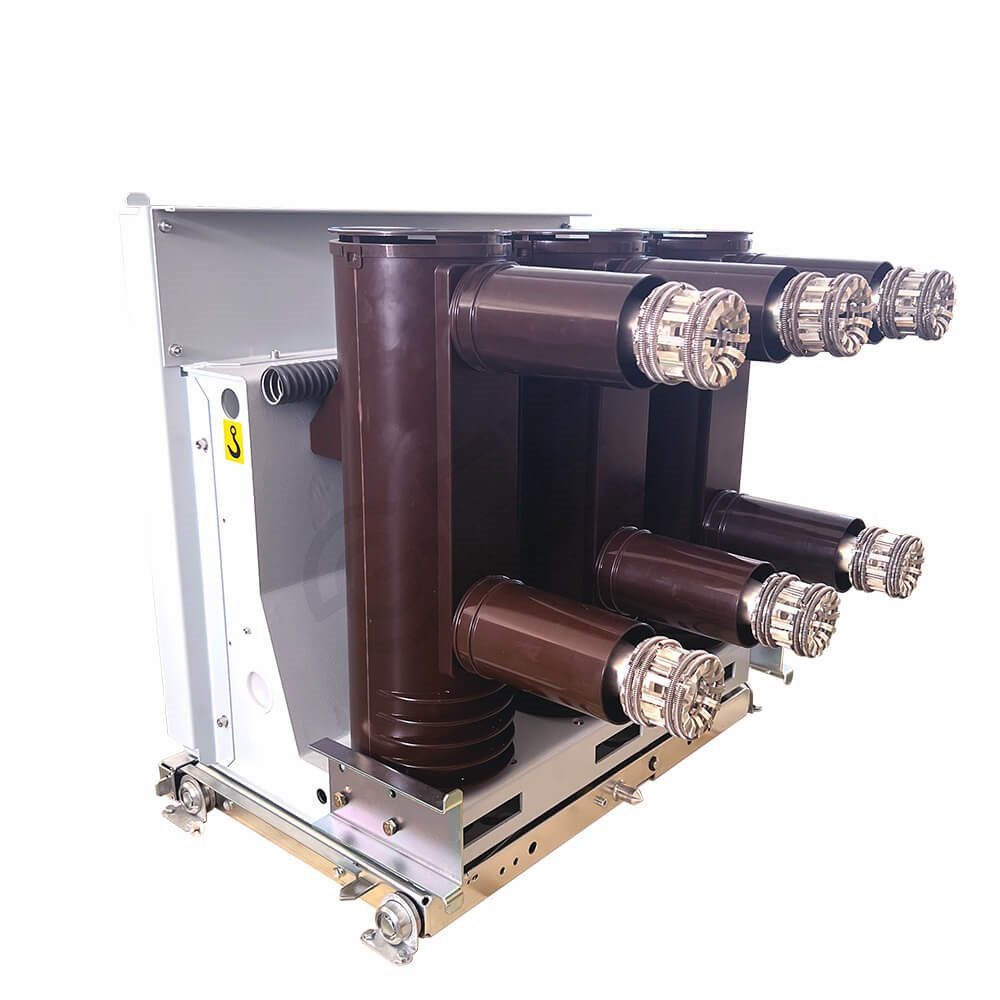

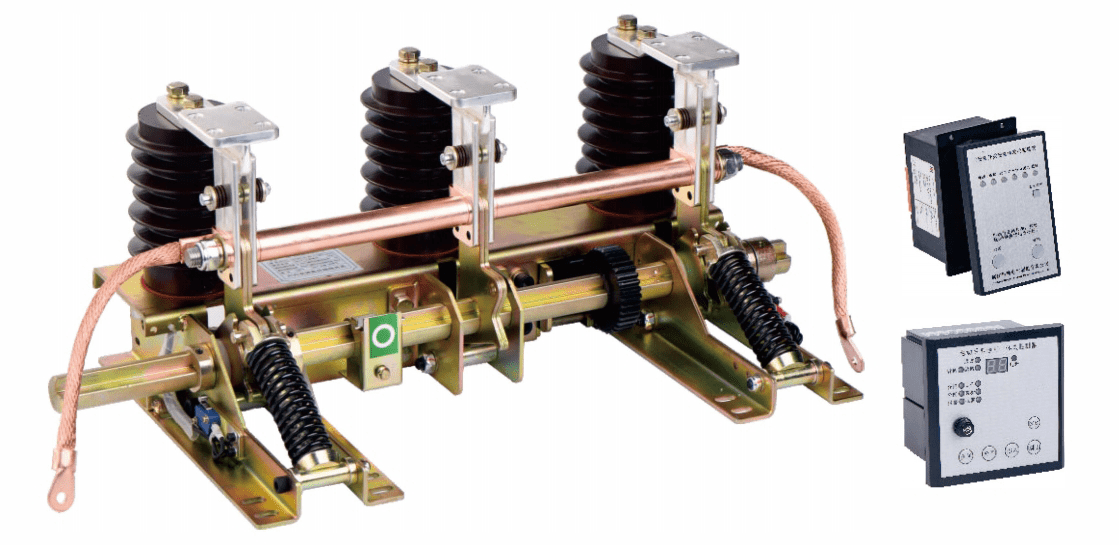 Earthing Switch/grounding switch is a crucial safety component in electrical systems. It provides a low-resistance path to the earth, ensuring safety by dissipating electrical energy and preventing electric shock hazards. It works alongside other protective devices during maintenance or fault conditions. Proper operation is vital for system integrity and personnel safety.
Earthing Switch/grounding switch is a crucial safety component in electrical systems. It provides a low-resistance path to the earth, ensuring safety by dissipating electrical energy and preventing electric shock hazards. It works alongside other protective devices during maintenance or fault conditions. Proper operation is vital for system integrity and personnel safety.
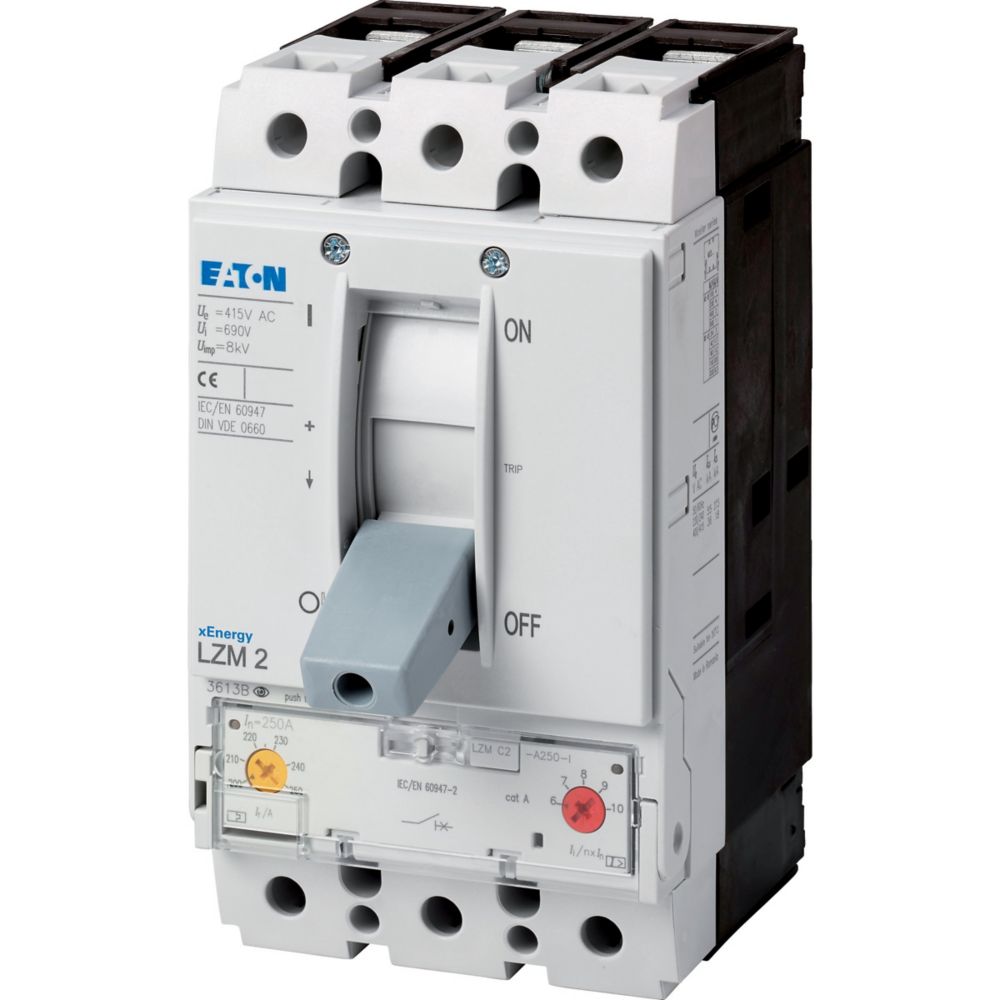


 LV Distribution refers to low voltage distribution systems. Common products in LV Distribution include MCCB, MCB, ACB, and RCCB. These products are used to protect circuits from overloads, short circuits, and residual currents, ensuring safe and stable power supply.
LV Distribution refers to low voltage distribution systems. Common products in LV Distribution include MCCB, MCB, ACB, and RCCB. These products are used to protect circuits from overloads, short circuits, and residual currents, ensuring safe and stable power supply.
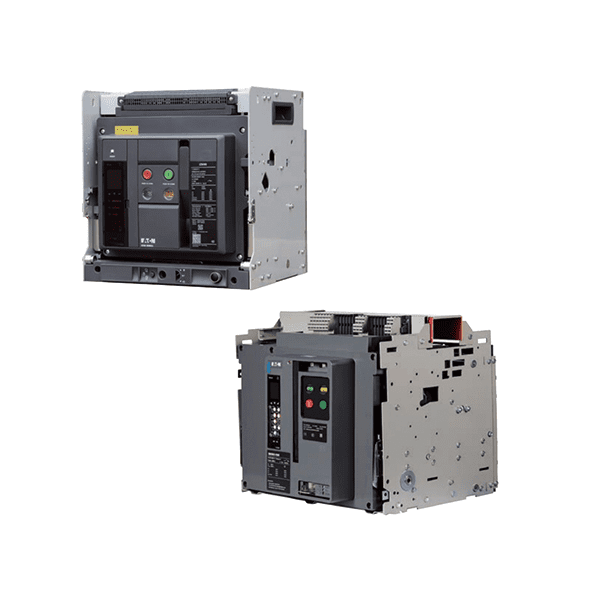 Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) is an electrical protection device used for short circuit and overcurrent protection up to 15kV with amperes rating of 800A to 10kA. It operates in air (where air-blast as an arc quenching medium) at atmospheric pressure to protect the connected electric circuits. ACB has completely replaced by oil circuit breaker because it is still a preferable choice to use an ACB because, there is no chance of oil fire like in oil circuit breaker.
Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) is an electrical protection device used for short circuit and overcurrent protection up to 15kV with amperes rating of 800A to 10kA. It operates in air (where air-blast as an arc quenching medium) at atmospheric pressure to protect the connected electric circuits. ACB has completely replaced by oil circuit breaker because it is still a preferable choice to use an ACB because, there is no chance of oil fire like in oil circuit breaker.






Make green power distribution more safe and efficient

Become a one-stop high-quality supply chain and professional service provider in the green power distribution

R&D, manufacturing, and production of SF6 Free RMU series of switches and switchgear.
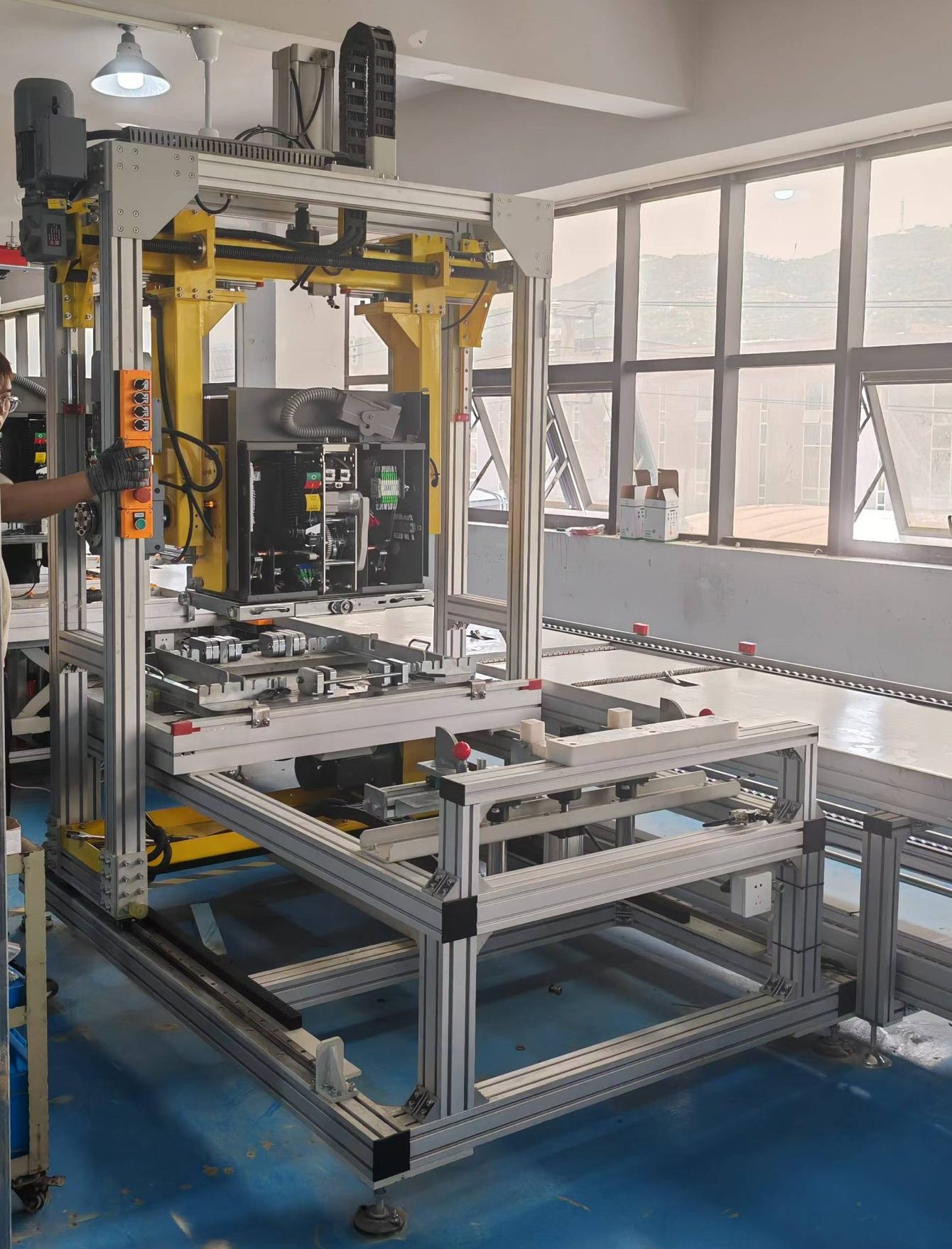

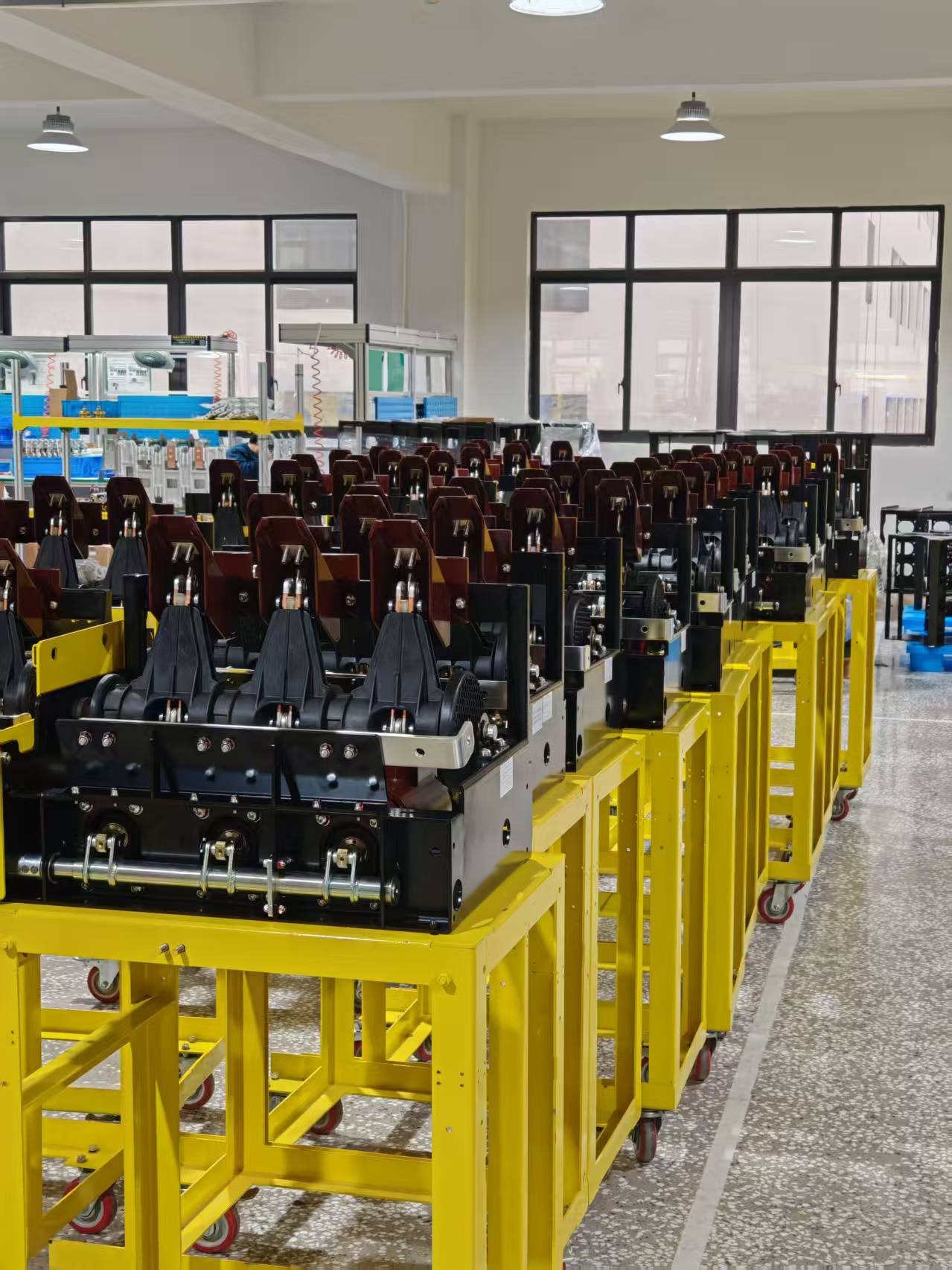
R&D, manufacturing and production of vacuum circuit breakers, side-mounted circuit breakers, circuit breaker mechanisms, etc.
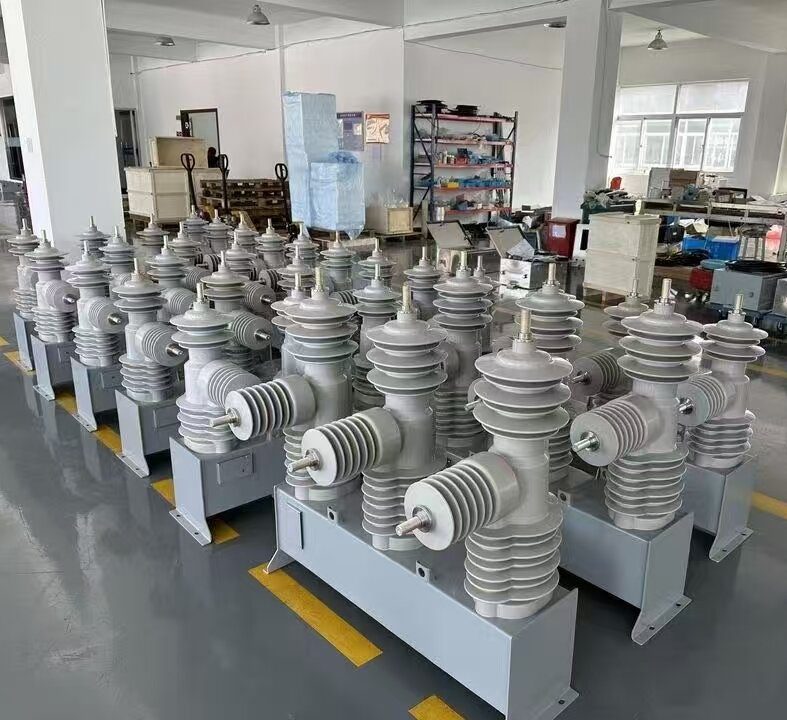

R&D, manufacturing and production of outdoor circuit breakers, reclosers, LBS, disconnectors, etc.





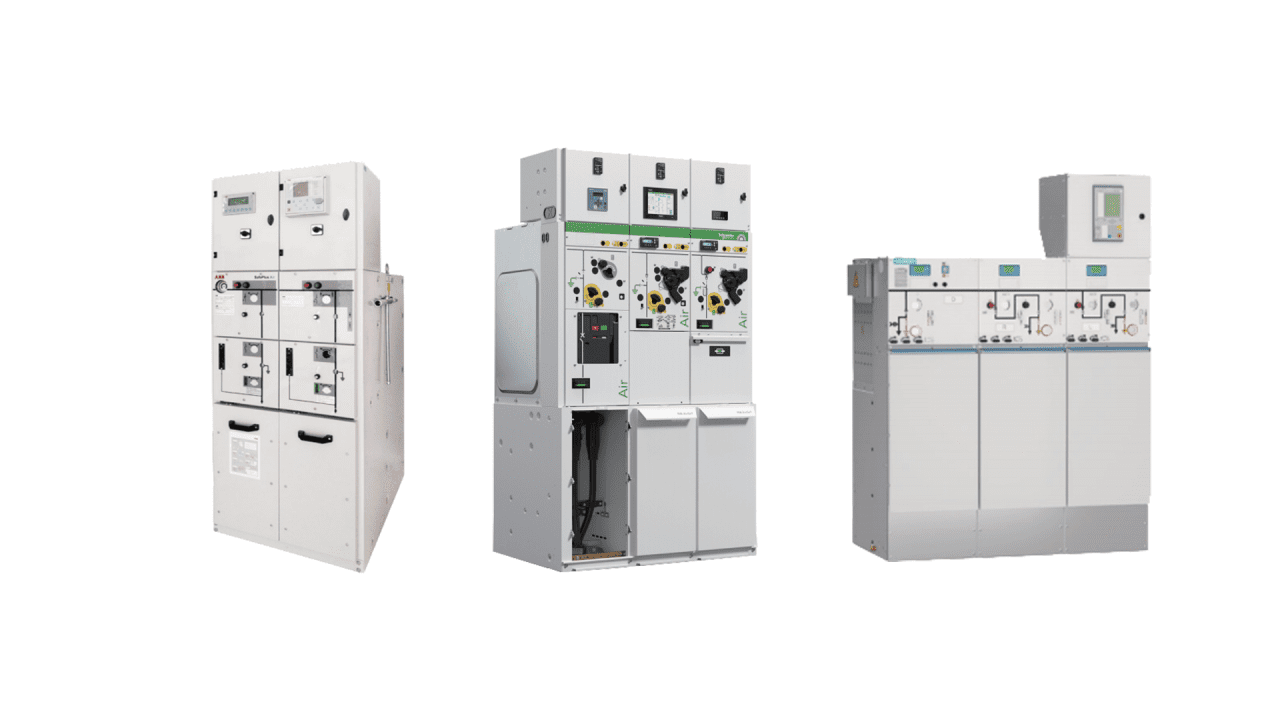
This is information about the current environmentally friendly switchgear from each of the three major brands (ABB, Schneider, Siemens). The
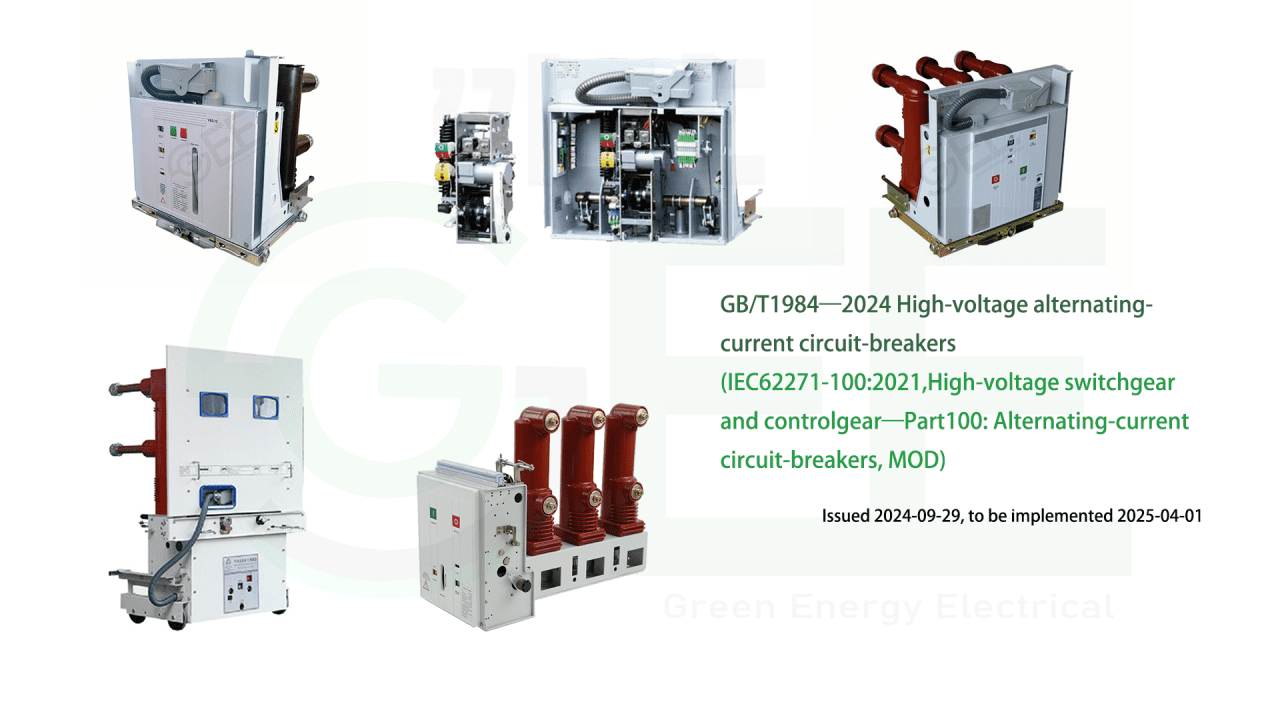
The latest version of GB/T1984—2024 High-voltage alternating-current circuit-breakers (IEC62271-100:2021, High-voltage switchgear and controlgear—Part 100: Alternating-current circuit-breakers, MOD) was released on

Vacuum circuit breakers have several advantages, including high interrupting capability, excellent arc-extinguishing performance, long mechanical and electrical life, low maintenance
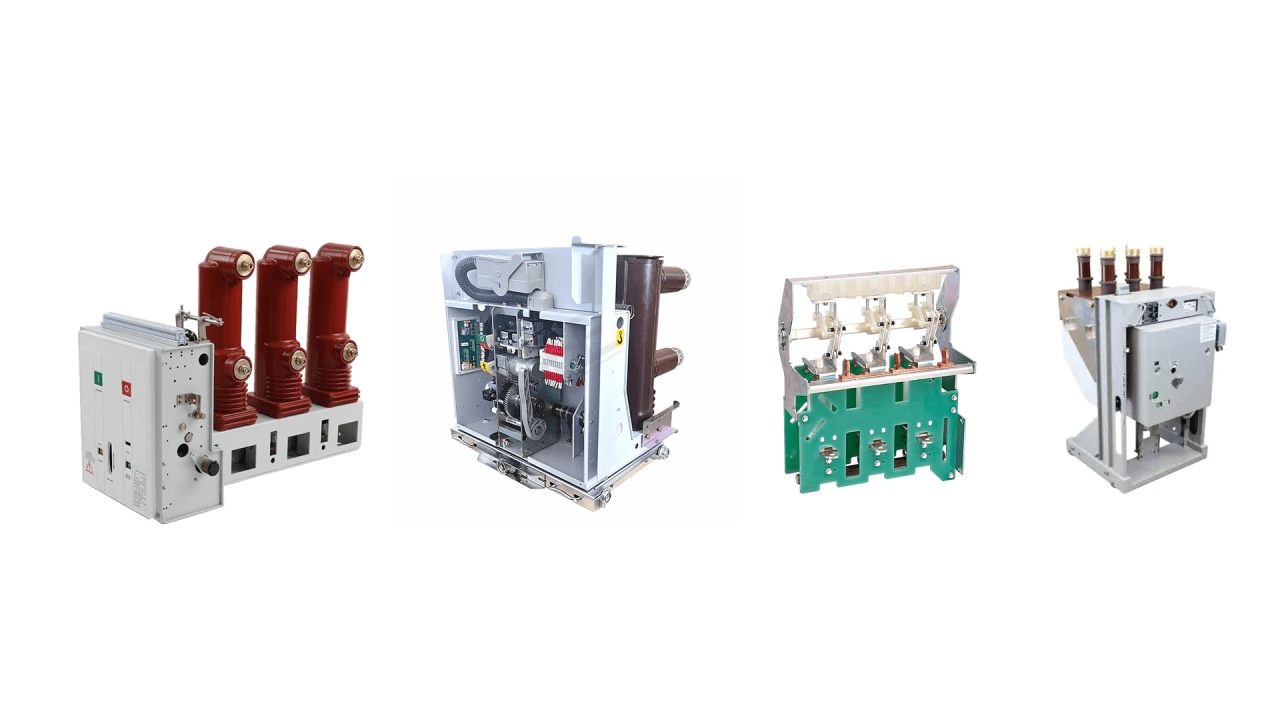
In switchgear applications, the withdrawable structure of circuit breakers can be divided into three main types, as detailed below: As
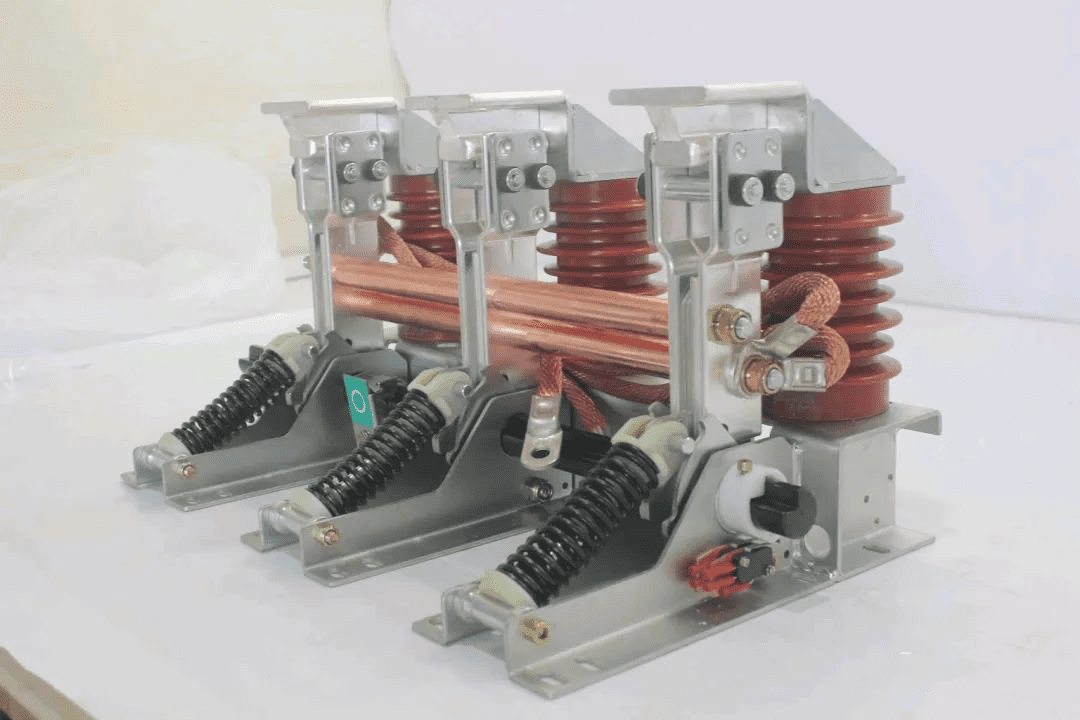
The MV grounding switch is an important part of the MV switchgear as the grounding protection of the high voltage

On behalf of GEE Company, we would like to extend our warmest New Year greetings to all. May this new

What we can provide is not just products, it’s a trust for quality, a demand for professional services, a partner to work with to cut cost and improve souring efficiency.
© 2025 Green Energy Electrical, All Rights Reserved.
Design by Zebuck